In today’s power-driven world, inverters have become essential components across homes, industries, and renewable energy systems. Their primary role is both simple and powerful: converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC), allowing everyday appliances and critical equipment to run smoothly. Whether supporting solar energy setups, powering devices in recreational vehicles, or backing up essential systems during outages, inverters lie at the heart of modern energy reliability and efficiency.
This comprehensive guide explains what an inverter is, how it works, where it’s used, and the benefits it brings—enhancing power stability, sustainability, and convenience.
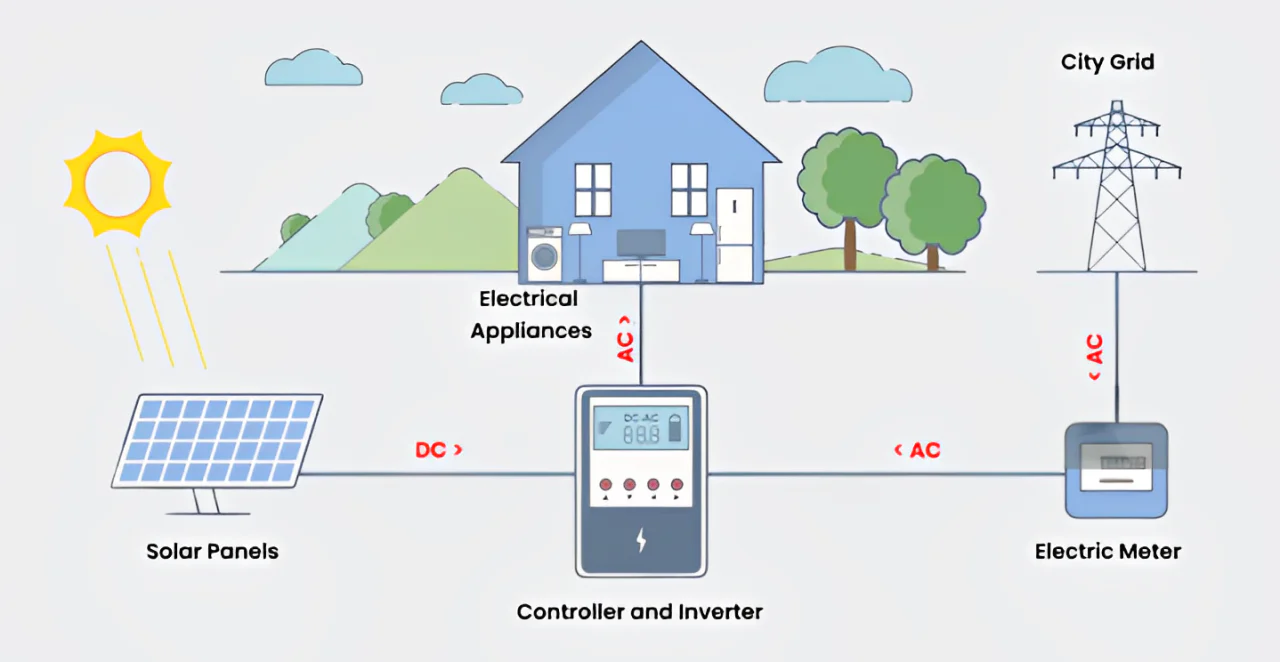
An inverter is an electronic device that converts DC electricity into AC electricity. Since most household appliances, electronic devices, and grid systems rely on AC power, inverters serve as the bridge that enables DC sources—such as batteries, solar panels, and wind turbines—to supply usable electricity.
Inverters come in a wide variety of sizes, ranging from small portable units for camping and emergencies to large-scale industrial models used in manufacturing plants and renewable energy farms. Their reliability and efficiency make them indispensable in modern power systems.
Although the fundamental role of an inverter is DC-to-AC conversion, its functionality extends well beyond that. Key applications include:
- Solar Energy Conversion: Solar panels produce DC electricity. Inverters convert this into AC power for use in homes, businesses, and the grid. They also help synchronize output with grid frequency and voltage.
- Backup Power Supply (UPS Systems): In uninterruptible power supply (UPS) setups, inverters automatically switch to battery power during outages, ensuring continuous operation of devices like computers and medical systems.
- Electric Vehicle Power Coordination: In electric vehicles, inverters regulate the flow of electricity between the battery and the motor, directly affecting performance, efficiency, and speed control.
- Power Conditioning and Voltage Regulation: Many modern inverters enhance power quality by stabilizing voltage, reducing electrical noise, and protecting against power surges.
- Smart Energy Management: Advanced inverters come with Wi-Fi connectivity for real-time monitoring, performance tracking, and remote control.
Thanks to these capabilities, inverters support energy independence, improve system reliability, and expand access to renewable power.
Inverters operate using electronic switching techniques that transform steady DC electricity into a waveform that mimics AC power.
Basic Operation:
1. The inverter receives DC input from a source such as a battery or solar panel.
2. Electronic components—typically transistors—switch the current direction rapidly to create electrical pulses.
3. These pulses are shaped and filtered to produce a smooth AC sine wave output.
Advanced Technology Used:
- Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM): Enables precise control of voltage and frequency, resulting in cleaner and more stable AC output.
- Microprocessor Controls: Monitor performance and adjust output in real time for greater efficiency.
- Pure Sine Wave Output Design: Ensures compatibility with sensitive electronics such as laptops, refrigerators, and medical devices.
The exact design and performance of an inverter depend on its intended use, capacity, and quality standards.
| Benefit | Description |
| Enables Renewable Energy Use | Converts solar and wind power into usable electricity |
| Supports Off-Grid & Backup Power | Maintains power supply during outages or in remote areas |
| Improves Power Quality | Regulates voltage and reduces harmonic distortion |
| Reduces Electricity Costs | Allows use of stored or self-generated energy, lowering utility bills |
| Smart Monitoring Features | Modern inverters support data tracking and remote access |
Inverters contribute to more resilient, sustainable, and cost-effective power systems.
- Home Backup Systems: Keep essential appliances running during power outages.
- Solar Energy Systems: Convert solar panel DC output into grid-compatible AC power.
- RVs, Boats, and Vehicles: Enable the use of household electronics while on the move.
- Portable Power Stations: Ideal for outdoor work, camping, and emergencies.
- UPS and IT Equipment: Provide backup power to prevent data loss and protect devices.
- Place the inverter in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated location.
- Only connect devices within the inverter’s recommended wattage range.
- For home solar systems, always use certified installers.
- Monitor power load to avoid overheating or automatic shutdown.
- Turn off the inverter before plugging or unplugging devices.
Inverters are vital to modern power systems, especially as the world shifts toward sustainable energy. They enable solar and wind systems to power homes and businesses, provide stable backup electricity, and support energy independence. As renewable energy adoption grows, inverters continue to evolve—offering greater efficiency, smarter grid connectivity, and enhanced reliability.
Choosing a high-quality inverter ensures optimal performance, a longer lifespan, and greater energy savings.
1. When do you need an inverter?
You need an inverter whenever you want to operate AC appliances using a DC power source, such as batteries or solar panels.
2. What does an inverter do in an RV?
It converts 12V DC power from the RV battery into AC power, allowing the use of standard household appliances without an external electrical supply.
3. How do I size a solar inverter?
Generally, the inverter should be rated at 1.1–1.3 times the total solar panel wattage to ensure stable and reliable power handling.
4. What types of solar inverters are available?
- Pure sine wave inverters: Ideal for all types of electronics, including sensitive devices.
- Modified sine wave inverters: More affordable but less compatible with sensitive equipment.
5. How long will a 12V battery run a 2000W inverter?
Runtime depends on battery capacity and the load applied. For a 100Ah battery under full load, expect around 30 minutes of operation. Lower loads will extend runtime.
Previous:FinDreams Battery CEO He Long Invited to Attend 9th China-Germany Automotive Conference