The cycle life of a LiFePO4 battery is determined by a series of physical and chemical interactions. Key factors affecting its longevity include:
Charging and Discharging
Using a charger with an appropriate cutoff mechanism is essential to prevent overcharging, which can shorten the life of a lithium iron phosphate battery. In general, slower charging rates are recommended to help extend battery life.
Depth of Discharge
The depth of discharge greatly affects how long a LiFePO4 battery lasts. Shallower discharges can significantly improve lifespan, while deep discharges tend to reduce it. It is best to avoid fully draining the battery to very low voltages.
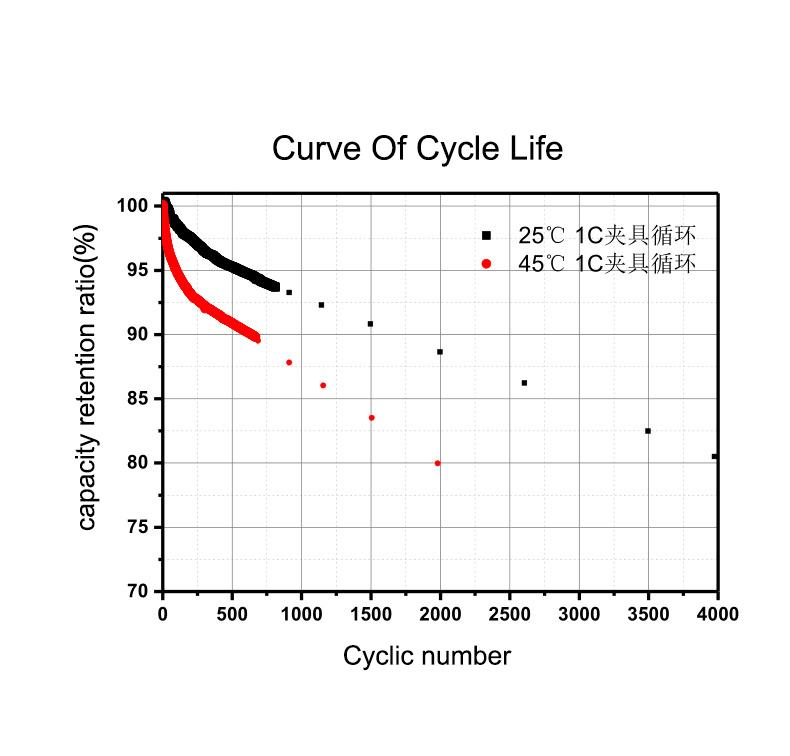
Temperature Conditions
High operating temperatures can degrade electrode activity in LiFePO4 batteries, reducing their service life. Keeping the battery within a moderate temperature range helps prolong its lifespan.
Under standard conditions, LiFePO4 batteries typically achieve over 2,000 cycles. Actual lifespan varies with usage intensity:
- Stable High C-rate Discharge: Common in high-power applications like motor drives, cycle life may be around 800 cycles.
- Unstable High C-rate Discharge: Irregular high-load use can shorten life to about 300 cycles.
Elevated temperatures challenge battery performance:
- Low Current Use: Quality batteries can exceed 1,000 cycles, while lower-quality ones may only reach about 500 cycles.
- Stable High C-rate Discharge: Even good batteries may not surpass 500 cycles under sustained high load due to faster material degradation.
- Unstable High C-rate Discharge: Frequent irregular use can further reduce life to 250–300 cycles.
Cold temperatures often impact batteries more severely than heat, potentially limiting cycle life to as low as 300 cycles under extreme cold conditions.
Battery life and performance can be evaluated through tests such as:
- Charge-Discharge Cycle Test: Simulates real use to assess stability over repeated cycles.
- Capacity Fading Test: Measures the battery's ability to hold charge over time.
- Temperature Performance Test: Checks functionality across different temperatures.
- Internal Resistance Test: Evaluates how resistance changes affect performance.
- Safety Performance Test: Ensures stability under abnormal conditions.
To maximize lifespan, consider these practices:
- Avoid deep discharges: maintain State of Charge between 20% and 80%.
- Follow optimal charging habits: refrain from frequent full charges and use a LiFePO4-compatible charger.
- Manage temperature: operate and store within recommended ranges.
- Control discharge rates: stay within suggested limits and use a Battery Management System (BMS) for monitoring.
- Store properly: keep batteries partially charged and avoid long inactivity.
- Ensure cell balance: use a BMS with balancing features and perform occasional equalization.
- Monitor regularly: track battery parameters via BMS and keep maintenance logs.
- Limit high-power demands: avoid or carefully manage high-drain applications to reduce wear.
Following these guidelines helps maintain performance and extend the service life of LiFePO4 batteries, making them a dependable choice for diverse applications.
Next:None
Previous:EVE Energy Shines with Marine Battery Safety Solutions at Marintec China 2025